US Struggles with Transformer Supply Shortages
Lead times and costs are expected to go up significantly
August 28, 2025
Follow Mercom India on WhatsApp for exclusive updates on clean energy news and insights
Power and distribution transformers in the U.S. are seeing supply deficits of 30% and 6% respectively, based on annual supply and demand estimates, according to a Wood Mackenzie report.
Transformer costs are likely to continue increasing with the imposition of U.S. trade tariffs, as the industry is highly dependent on imports for both finished equipment and underlying components and commodities.
Not only will the average cost per transformer increase significantly due to the tariffs, but lead times will grow as imports from high-tariff countries become cost-prohibitive.
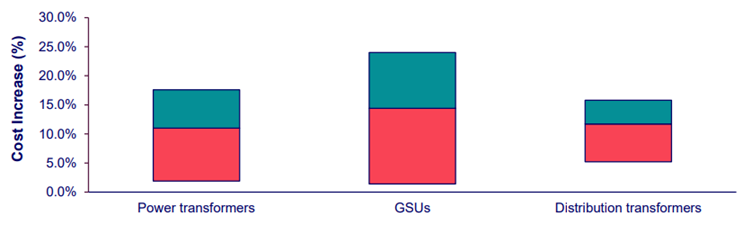
“The ongoing market deficit, combined with the aggressive trade policy, will continue putting upward pressure on U.S. transformer prices over the coming years. We calculate that prices will jump by a further 20% to 30% depending on the specification, further straining project costs.”
Impacts range from less than 2% to over 15% depending on the transformer type and tariff scenario.
The tariffs factored into each case are as follows:
- Base case: includes existing tariffs as of August 2025, including the new 50% copper tariff, 50% Indian and Brazil tariff, and 35% on non-U.S.-Mexico-Canada Agreement-compliant imports from Canada
- Low case: represents the unsuccessful appeal of the tariff ban, which would revert to 50% commodity-specific tariffs only
- High case: includes all tariffs factored into the base case as well as additional tariffs on countries without an agreement, including China and the European Union
Many of the largest transformer original equipment manufacturers have announced capacity expansions worth $1.8 billion since 2023 to address the market shortage. However, the demand growth rate will require even more investment to rebalance the market.
Transformer Demand Surge
Transformer demand in the U.S. has surged due to a 7% rise in electricity consumption between 2010 and 2020. This growth has been driven by rapid data center expansion, a nearly doubling of manufacturing construction spending due to the tax incentives of the 2022 Inflation Reduction Act, and widespread electrification.
Ageing equipment is adding to the shortage. A 2024 Department of Energy study found that 40 million units, or 55% of in-service distribution transformers, were over 33 years old and well beyond their service life. An increase in extreme weather events has heightened the risks to grid reliability. Domestic manufacturing capacity has been unable to keep pace with the growing demand.
Wood Mackenzie stated that utilities are increasingly relying on imports, with estimates suggesting that imports account for 80% of U.S. power transformer supply and 50% of distribution transformer supply.
This trend is most evident in power and generation step-up transformers, where demand is estimated to have increased 116% and 274%, respectively, since 2019. Even distribution transformers, which comprise nearly 98% of transformer demand on a unit basis, have seen growth ranging from 30% to 80%.
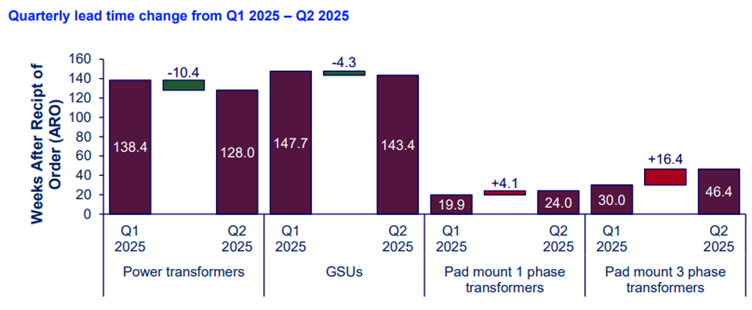
Long Lead Times
The shortage has led to a significant rise in both lead times and prices in most transformer categories. Since 2019, unit costs have risen by 45% for generation step-up, 77% for power, and 78% to 95% for distribution transformers. However, higher-voltage units have seen larger U.S. dollar-based cost escalations due to higher baseline costs.
Wood Mackenzie also highlighted market volatility for grain-oriented electrical steel, for which prices have reached all-time highs. The U.S. relies on a single domestic supplier, forcing many original equipment manufacturers to import raw electrical steel or semi-finished transformer cores.
Copper windings have emerged as another potential bottleneck to transformer production, due to their highly technical manufacturing process and niche specifications. The U.S. government’s 50% copper tariffs are likely to worsen the issue.
Besides the shortage of specialist technical manpower in transformer manufacturing, the domestic sector is cautious about expanding capacity due to uncertainties caused by the “One Big Beautiful Bill.”
The U.S. Treasury Department recently announced new rules to limit wind and solar companies from claiming federal tax breaks. It also obligated utility-scale projects to conduct off-site physical work tests for power equipment, including transformers.
The Indian renewable energy industry is also grappling with transformer shortages, as renewable energy installations and pipelines continue to rise consistently. Last year, Mercom reported that solar projects were being delayed due to longer lead times for power transformers.