Solar and Wind to Account for 21% of U.S. Power Generation by 2027: EIA
Most of the utility-scale solar capacity additions are expected to be commissioned in Texas
January 22, 2026
Follow Mercom India on WhatsApp for exclusive updates on clean energy news and insights
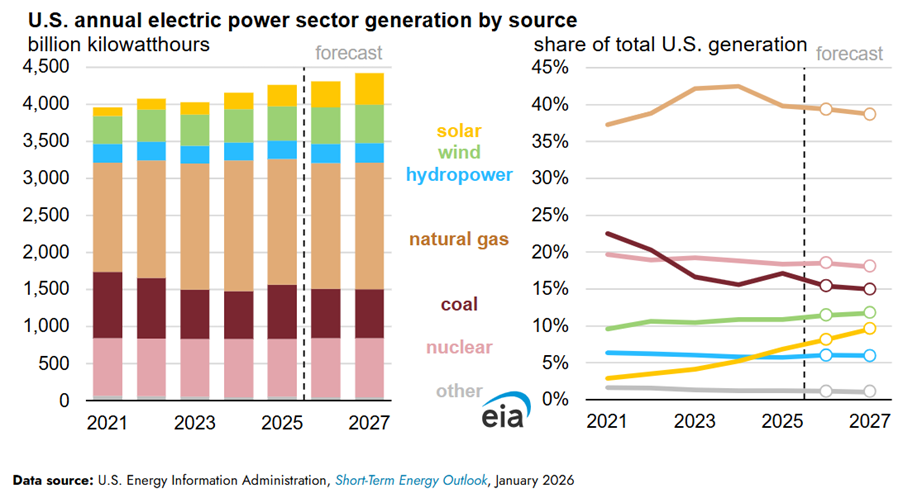
Utility-scale solar is the fastest-growing energy source in the U.S., with an expected increase to 424 billion kWh by 2027, up from 290 billion kWh in 2025, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration’s (EIA) Short-Term Energy Outlook report.
The U.S. electric power generation reached 4,620 billion kWh in 2025, and is projected to grow by 1.1% in 2026 and 2.6% in 2027, reaching an annual total of 4,423 billion kWh.
Natural gas, coal, and nuclear energy accounted for 75% of electricity generation in 2025. However, EIA expects this to fall to 72% by 2027, with solar and wind electricity rising to 21% by then, from 18% in 2025.
EIA had earlier predicted that solar would likely account for more than half of the 64 GW of new utility-scale electricity that developers plan to bring online in the U.S. in 2025.
The U.S. plans to commission nearly 70 GW of new solar projects in 2026 and 2027. This represents a 49% growth in the U.S. from 2025.
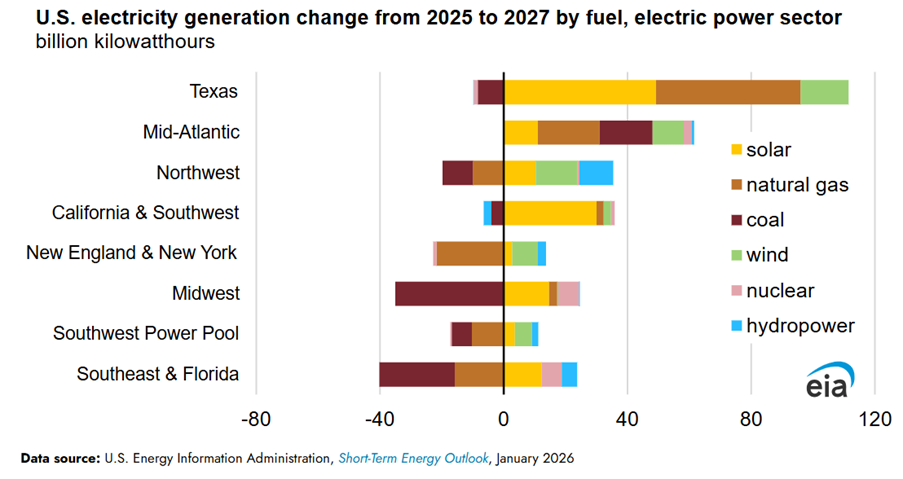
Most of the utility-scale solar capacity additions are expected to be commissioned in Texas. EIA projects that solar energy supplied to the grid managed by the Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT) will grow from 56 billion kWh in 2025 to 106 billion kWh in 2027.
The Midcontinent Independent System Operator (MISO) is forecasted to increase its solar generation capacity to 46 billion kWh in 2027, up from 31 billion kWh in 2025.
ERCOT will receive support to address fluctuations in daytime solar output from increasing battery storage capacity. The electric power sector’s battery capacity expansion plan aims to reach 37 GW by the end of 2027, up from 15 GW in 2025.
EIA said wind generation has typically been concentrated in the U.S. central regions, including the MISO-operated grid. However, new wind capacity additions have slowed in MISO, with only a marginal average annual growth of 100 billion kWh expected through 2027.
Utility-scale projects in the U.S. remained the primary contributor to solar expansion in 2024, accounting for 80% of new solar and 54% of all new capacity additions, according to a report by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.